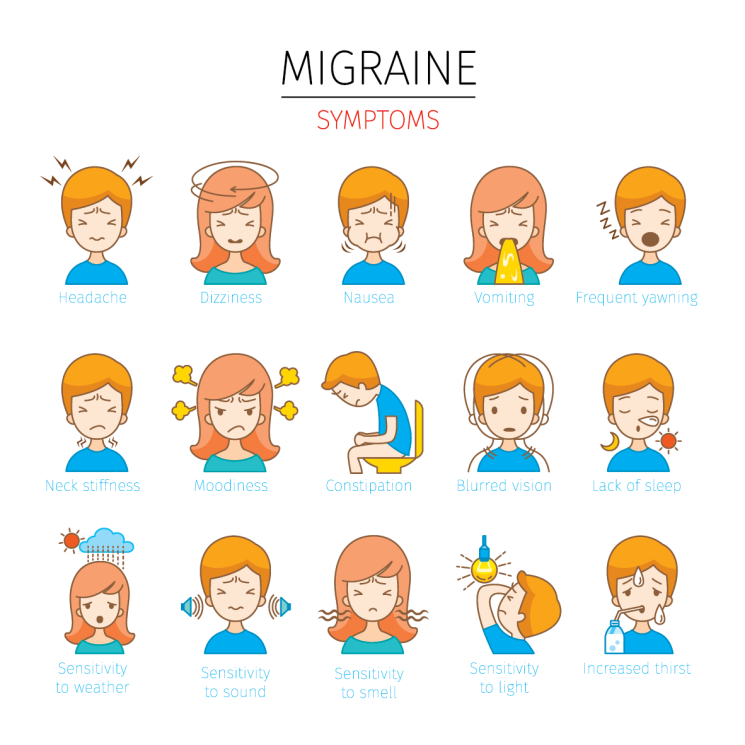
Migraines are a neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite the prevalence of migraines, there are many myths and misconceptions about the condition that can lead to confusion and frustration for those who suffer from it. In this article, we’ll explore some of the most common myths and misconceptions about migraine symptoms and help to debunk them.
Myth #1: Migraines are just really bad headaches.
One of the biggest misconceptions about migraines is that they are just really bad headaches. While migraines do involve head pain, they are much more complex than a simple headache. Migraines are a neurological disorder that can cause a range of symptoms beyond head pain, including nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances.
Myth #2: Migraines only affect women.
While it’s true that women are more likely to suffer from migraines than men, men can and do get migraines. In fact, around 12% of the US population suffers from migraines, and about half of those are men. Migraines are a neurological disorder that can affect anyone, regardless of gender.
Myth #3: Migraines are caused by stress.
While stress can trigger migraines in some people, it’s not the underlying cause of the condition. Migraines are thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including changes in brain chemicals, hormone fluctuations, and certain foods or drinks. Stress can exacerbate migraines in some people, but it’s not the sole cause of the condition.
Myth #4: Migraines are a sign of a weak constitution.
This myth is not only untrue, but it’s also harmful. Migraines are a neurological disorder that can affect anyone, regardless of their strength or constitution. There is no evidence to suggest that people who suffer from migraines are weak or less capable than those who don’t.
Myth #5: You can cure migraines with over-the-counter painkillers.
While over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide relief for some people, they are not a cure for migraines. Migraines are a neurological disorder that requires a comprehensive approach to treatment. This may include prescription medications, lifestyle changes, and other therapies.
Myth #6: Migraines always involve auras.
While auras can be a common symptom of migraines, not everyone who suffers from migraines experiences them. Auras are a type of visual disturbance that can include flashing lights, zigzag lines, or blind spots. They can occur before, during, or after a migraine, but they are not present in all cases.
Myth #7: Migraines are just a part of getting older.
While it’s true that migraines can become more common as we age, they are not an inevitable part of the aging process. Migraines are a neurological disorder that can affect people of all ages, from children to the elderly.
Myth #8: Migraines can be cured with alternative medicine.
While alternative medicine may provide some relief for some people, there is no cure for migraines. Migraines are a complex neurological disorder that requires a comprehensive approach to treatment. While alternative therapies may be a part of a comprehensive treatment plan, they are not a cure for the condition.
Myth #9: Migraines are not a serious condition.
Migraines can be a debilitating condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. They can cause severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and other symptoms that can make it difficult to perform daily activities. In some cases, migraines can be so severe that they require hospitalization.
Myth #10: Migraines can be prevented by avoiding trigger foods.
While certain foods and drinks can trigger migraines in some people, avoiding these triggers is not a foolproof method for preventing migraines. Migraines are a complex neurological disorder that can have many triggers, including changes in weather, hormonal fluctuations, and stress. While avoiding trigger foods may be a part of a comprehensive treatment plan, it is not a cure or prevention method for migraines.
Myth #11: Migraines are always preceded by warning signs.
While some people may experience warning signs before a migraine, not everyone does. Migraines can come on suddenly without any warning signs, making it difficult to predict when they will occur.
Myth #12: Migraines are not treatable.
While there is no cure for migraines, there are many effective treatments available. These may include prescription medications, lifestyle changes, and other therapies. With proper treatment, many people with migraines are able to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Myth #13: Migraines are not a disability.
Migraines can be a disabling condition that can impact a person’s ability to perform daily activities. In some cases, migraines can be so severe that they prevent a person from working or participating in social activities. Migraines are recognized as a disability under the Americans with Disabilities Act, and people with migraines may be entitled to accommodations at work or school.
Myth #14: Migraines are not hereditary.
While the exact cause of migraines is not fully understood, there is evidence to suggest that they may have a genetic component. Studies have shown that migraines tend to run in families, and people with a family history of migraines may be more likely to develop the condition.
Myth #15: Migraines can be cured by surgery.
While surgery may be a treatment option for some types of migraines, it is not a cure for the condition. Surgery is typically reserved for people with chronic migraines who have not responded to other treatment options. Even in these cases, surgery is not a guarantee and may not provide complete relief from migraines.
In conclusion, migraines are a complex neurological disorder that can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. While there are many myths and misconceptions about the condition, it’s important to seek accurate information and treatment options from qualified healthcare professionals. With proper treatment and management, many people with migraines are able to improve their symptoms and lead full, productive lives.






