Pancreatic cancer is often referred to as the “whispering assassin” because it tends to hide in the shadows, silently advancing before manifesting noticeable symptoms. Understanding the subtleties of these symptoms is crucial for early detection, as pancreatic cancer is notorious for its late-stage diagnosis and high mortality rate. In this article, we will delve deep into the enigmatic world of pancreatic cancer symptoms, shedding light on its covert nature and the importance of recognizing these signs. Let’s embark on this journey to decipher the whispers of pancreatic cancer and raise awareness about the critical need for vigilance.
1. The Unseen Intruder: Pancreatic Cancer Unveiled
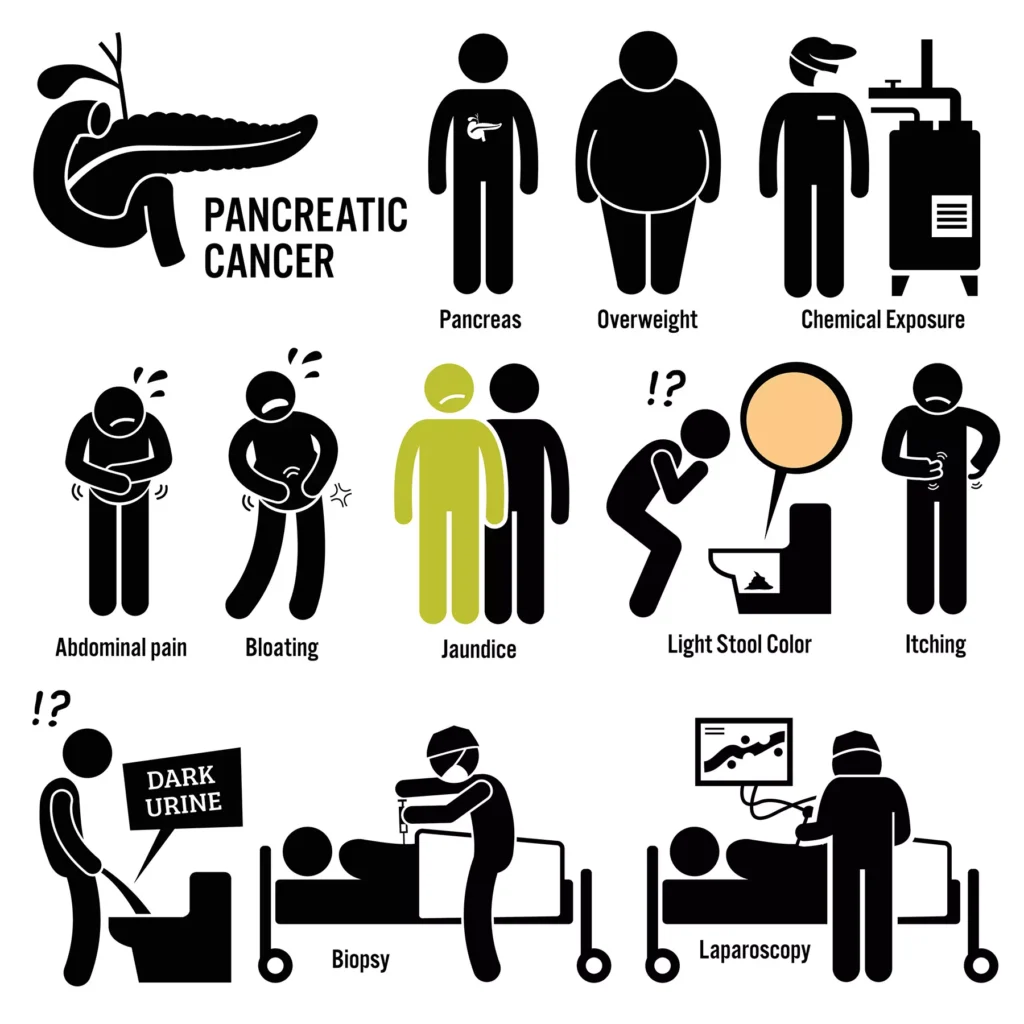
Pancreatic cancer, a malignant disease that affects the pancreas, can be insidious in its onset. The pancreas, a vital organ located behind the stomach, plays a crucial role in digestion and hormone regulation. However, when cancer invades this organ, it can disrupt its normal functions and lead to a cascade of symptoms.
2. The Silent Onset: Early Pancreatic Cancer Symptoms
Early-stage pancreatic cancer often proceeds without any conspicuous symptoms, making it challenging to detect. Nevertheless, some subtle signs may give an inkling that something is amiss within the pancreas.
2.1. Unexplained Weight Loss
Sudden, unexplained weight loss is a common early indicator of pancreatic cancer. When cancer disrupts the pancreas’s ability to produce digestive enzymes, the body struggles to absorb nutrients, leading to unintended weight loss.
2.2. Abdominal Pain
Pancreatic cancer can cause discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen or back. This pain may be dull and persistent, worsening after meals or when lying down. It is often mistaken for other less severe conditions.
2.3. Jaundice
Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, can occur when pancreatic cancer obstructs the bile duct. This obstruction leads to a buildup of bilirubin in the bloodstream, resulting in the classic yellow hue associated with jaundice.
3. The Hidden Culprit: Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Symptoms
As pancreatic cancer advances, the symptoms become more pronounced and alarming, demanding immediate attention.
3.1. Dark Urine and Pale Stools
The blockage of the bile duct due to pancreatic cancer can also cause changes in urine and stool color. Dark urine and pale stools may signal an issue with the pancreas or bile duct, which should be investigated promptly.
3.2. Loss of Appetite and Nausea
Advanced pancreatic cancer can further disrupt the digestive process, leading to a loss of appetite and persistent nausea. This can make it difficult for individuals to maintain their normal eating habits.
3.3. Blood Clots
Pancreatic cancer can increase the risk of blood clots, leading to conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE). If you experience sudden pain, swelling, or redness in your limbs, seek medical attention immediately.
3.4. Diabetes Onset or Worsening
In some cases, pancreatic cancer can affect the production of insulin, resulting in the development of diabetes or the worsening of pre-existing diabetes. This sudden change in blood sugar levels should be investigated by a healthcare professional.
4. The Elusive Diagnosis: Pancreatic Cancer and its Mimickers
One of the challenges in diagnosing pancreatic cancer is its ability to mimic other, less severe conditions. This can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Let’s explore some conditions that may be mistaken for pancreatic cancer.
4.1. Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas, shares symptoms such as abdominal pain and nausea with pancreatic cancer. A careful evaluation by a healthcare provider is necessary to differentiate between the two.
4.2. Gallstones
Gallstones can also cause abdominal pain and jaundice, making it easy to confuse their symptoms with those of pancreatic cancer. Imaging studies can help determine the underlying cause.
4.3. Gastrointestinal Disorders
Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or gastritis can lead to weight loss and digestive discomfort, similar to early pancreatic cancer symptoms. A thorough examination is essential to rule out cancer.
5. The Importance of Early Detection: Pancreatic Cancer Screening
Given the elusive nature of pancreatic cancer symptoms, early detection becomes paramount for improving survival rates. While there is no routine screening test for pancreatic cancer, certain individuals with risk factors should consider regular check-ups and discussions with their healthcare providers.
5.1. Family History
Individuals with a family history of pancreatic cancer are at an increased risk. Close relatives, such as parents, siblings, or children, who have had pancreatic cancer may indicate a hereditary predisposition. Genetic counseling and screening may be recommended in such cases.
5.2. Inherited Genetic Syndromes
Certain genetic syndromes, such as Lynch syndrome and familial atypical multiple mole melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome, are associated with an elevated risk of pancreatic cancer. Those with a family history of these syndromes should undergo regular screenings.
5.3. Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis, especially if it develops at a young age, can increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer. Patients with chronic pancreatitis should be closely monitored.
5.4. Smoking and Obesity
Smoking and obesity have been linked to an increased risk of pancreatic cancer. Lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy weight, can help reduce this risk.
6. The Detective Work: Diagnosis and Treatment
When pancreatic cancer is suspected, a series of diagnostic tests are conducted to confirm the presence of the disease and determine its stage. These tests may include:
6.1. Imaging Scans
CT scans, MRI scans, and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) can provide detailed images of the pancreas, helping doctors assess the tumor’s size, location, and spread.
6.2. Biopsy
A biopsy involves the removal of a small tissue sample from the pancreas for examination under a microscope. It is the definitive way to confirm the presence of cancer.
6.3. Blood Tests
Blood tests may reveal elevated levels of specific tumor markers, such as CA 19-9, which can indicate the presence of pancreatic cancer.
7. The Battle Plan: Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
The treatment approach for pancreatic cancer depends on its stage, location, and the patient’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
7.1. Surgery
Surgery aims to remove the tumor and, in some cases, a portion of the pancreas. Surgical options may include a Whipple procedure, distal pancreatectomy, or total pancreatectomy.
7.2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other particles to target and destroy cancer cells. It may be used before or after surgery or in combination with chemotherapy.
7.3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth. It can be administered before or after surgery or as a standalone treatment for advanced cases.
7.4. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy drugs are designed to target specific molecules involved in cancer growth. They may be used in conjunction with chemotherapy.
8. The Outlook: Living with Pancreatic Cancer
A diagnosis of pancreatic cancer can be daunting, but it’s essential to remember that advances in medical research and treatment options continue to improve the outlook for patients. Support from healthcare professionals, friends, and family is invaluable during this journey.
8.1. Clinical Trials
Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and therapies that may offer hope for improved outcomes.
8.2. Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on providing relief from the symptoms and side effects of cancer treatment. It can enhance the quality of life for individuals living with advanced pancreatic cancer.
9. The Final Word: Awareness Saves Lives
In the realm of pancreatic cancer, awareness is the key to early detection and improved survival rates. Understanding the subtle signs and risk factors associated with this disease empowers individuals to take action and seek timely medical attention.
Conclusion
Pancreatic cancer may be a silent intruder, but with knowledge and vigilance, its whispers can be heard. Recognizing the subtle symptoms and risk factors associated with this disease is the first step towards early detection and effective treatment. By shedding light on the enigmatic world of pancreatic cancer symptoms, we hope to inspire awareness, encourage early diagnosis, and ultimately save lives. In the battle against the “whispering assassin,” knowledge is our most potent weapon.




